Financial Document Processing with AI
Fast, efficient, and reliable financial document processing powered by state of the art generative AI and Natural Language Processing techniques.
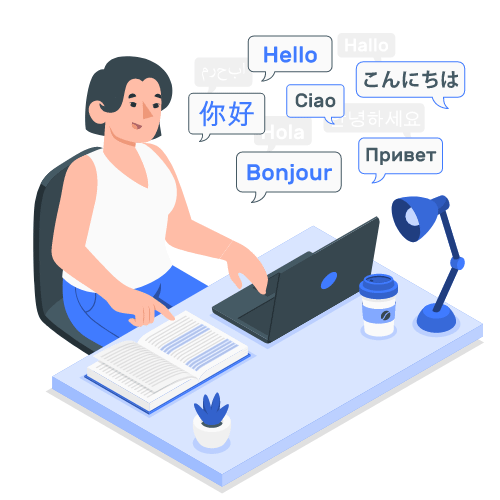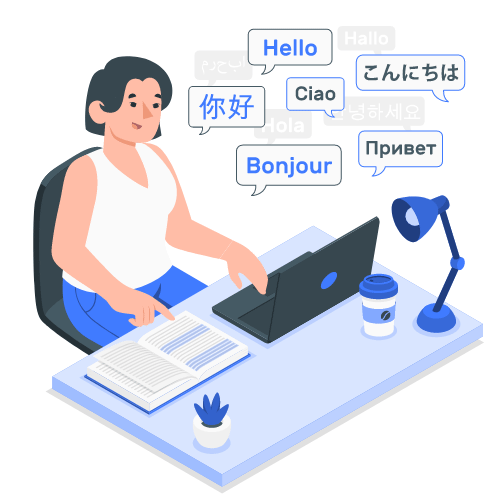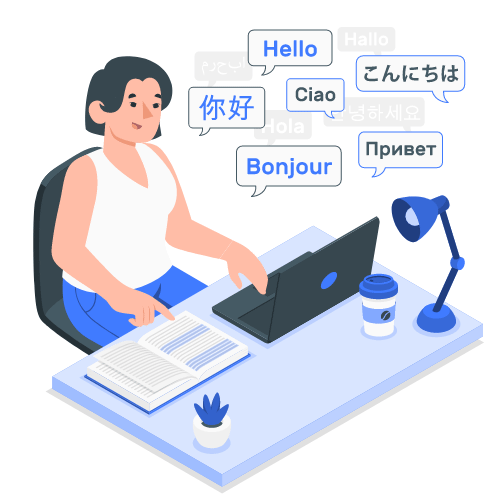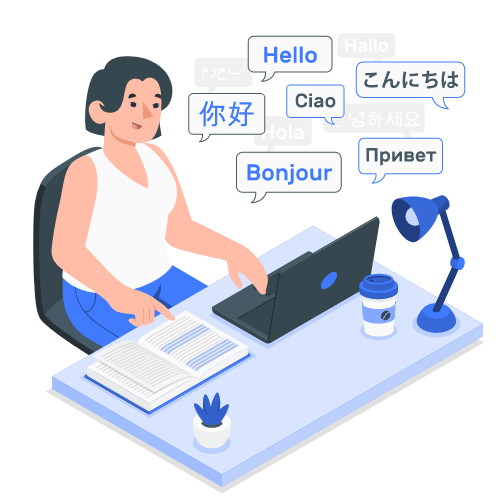
Translation, transcription and analytical tools to help you understand, communicate and extract the information contained in financial documents within seconds to add value and boost your productivity or propose new services to your clients.
Tailored document processing solutions for the financial industry leveraging the power of generative AI, accessible through a secure platform or API.
Document Processing
Direct access to our user-friendly and secure platform offering Generative A.I document processing solutions or via API for industrial volumes of data.
AI Advisory
Expert guidance on customisation and development of Large Language Models (LLMs) for your company.
Recent case studies showcasing how our generative AI solutions address financial document processing challenges and add value.

Translation
Global issues on subject matters in translation

Data Extraction
Rapid analysis and data extraction

Transcription
Financial Meeting Transcription
Struggling with data overload? Looking for a financial document processing service which can optimise your productivity? Our AI services enable you to:
SECURE
Your sensitive information remains secure and confidential with Lingua Custodia. We prioritise the protection of your data by ensuring it is never handled by third parties. Our dedicated servers are exclusively located in France, adhering to EU compliance standards. To guarantee the highest level of security, our dedicated on-site team continuously monitors, supervises, and safeguards these servers.

ANALYSE
Lingua Custodia's advanced AI algorithms allow you to swiftly unlock insights regarding both financial and non financial data to identify trends and relationships mapping for informed decision-making purposes.
COMMUNICATE
Leverage our translation services to rapidly communicate and share financial documents such as KIDs and fund reports in over 10 different languages. Our transcription services help you to rapidly transcribe and share your round table, conferences and podcasts events in over 36 different languages.
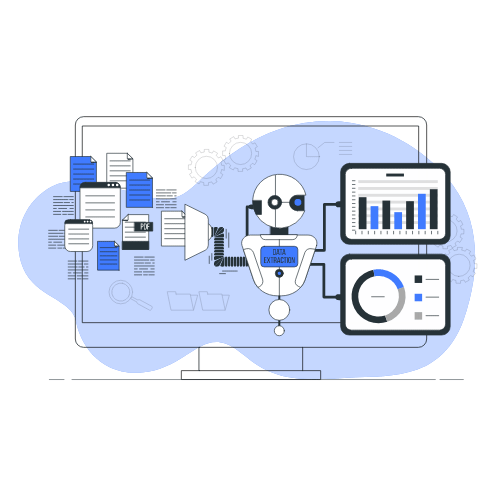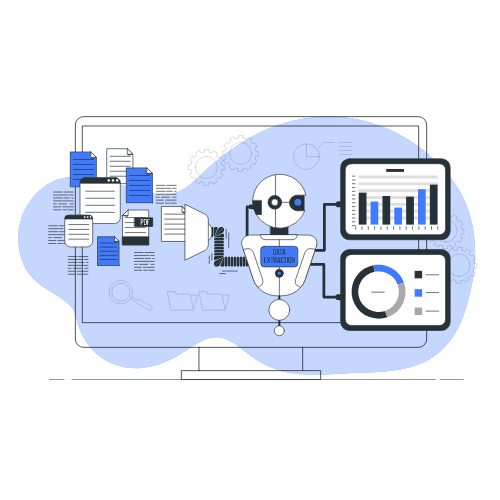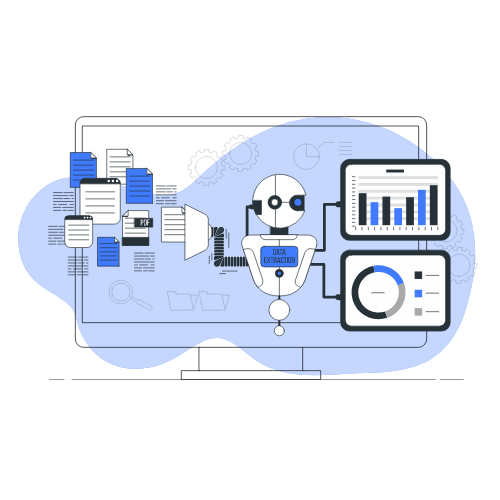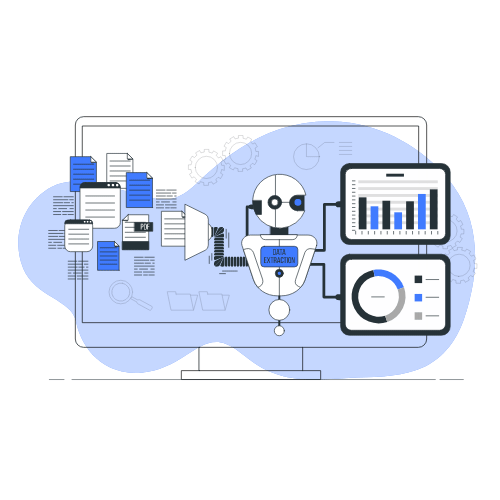
EXTRACT
Our generative AI Document Analyser tool allows you to swiftly extract key data from large documents and can be used to answer due diligence queries.The PDF table extractor enables you to effortlessly extract and analyse data from financial documents, in order to explore different financial scenarios and to gain a detailed understanding of key financial ratios.
Our generative AI solutions for document processing are innovative, effective, customisable and secure.